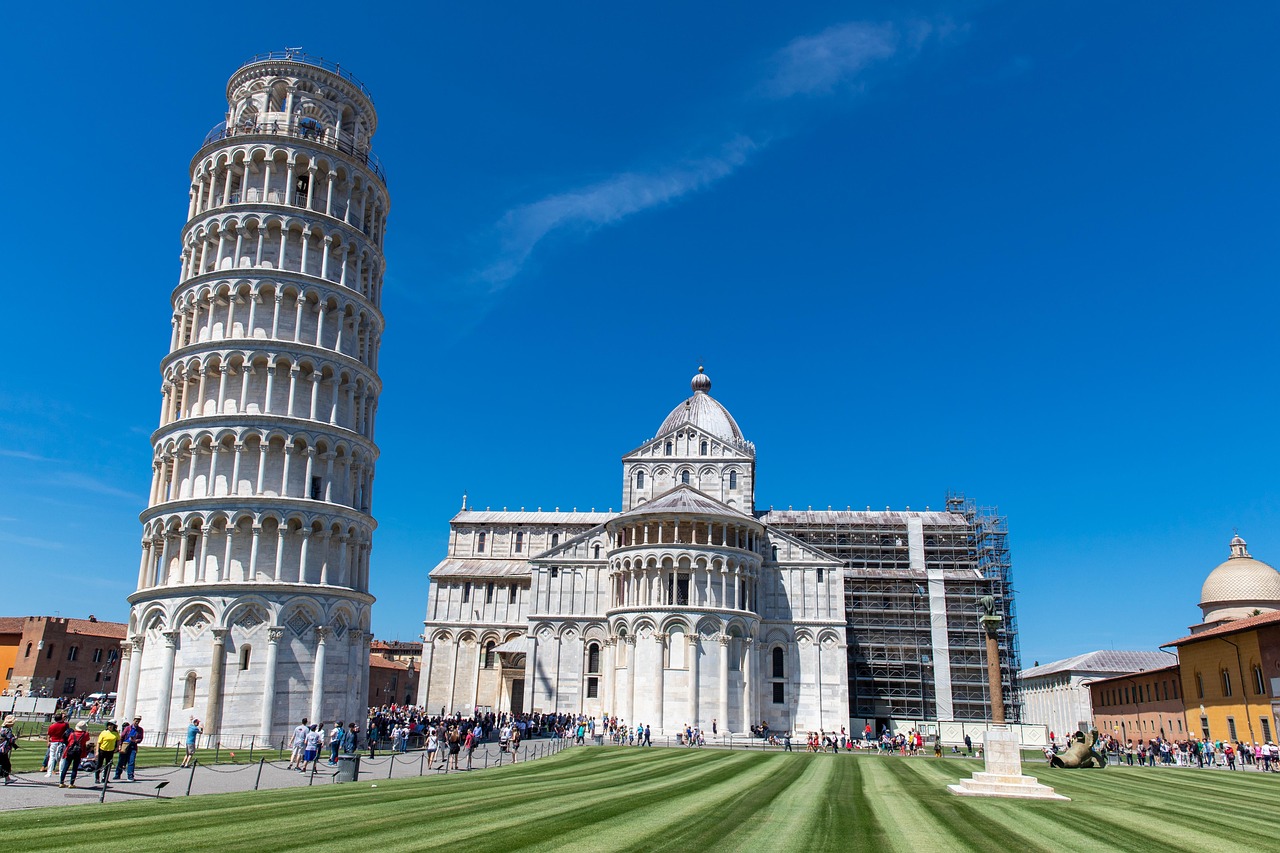
イタリアの世界遺産として名高いピサの斜塔。ピサの斜塔は有名なドゥオモ広場(1987年からユネスコ世界遺産に登録)にあるサンタ・マリア・アッスンタ大聖堂の鐘楼である。塔の中には7つの鐘があります。
なぜピサの塔は斜めっているのでしょうか。実は建設地の地盤の問題にあります。。
建設は1173年に開始しましたが、それよりも何年も前には海に近い湿地帯でした。そのため、地盤が非常に軟弱だったのです。塔の基礎は、わずか3メートルほどの深さしかありませんでした。これは、当時の技術では、深礎を掘ることは難しかったためですが、塔の重量を支えるには明らかに不十分でした。傾きに気づいた建設者たちは、一時的に工事を中断しました。しかし、約100年後に工事が再開されました。建設中に傾き始めたことに対応し、上層部を傾きと反対側にわずかに曲げて建設されました。これは塔全体のバランスを調整し、安定性を高める効果があります。長年にわたる傾斜により、塔の基盤となる地盤が徐々に圧縮され、強度が増しました。さらに、20世紀末から21世紀初頭にかけて行われた大規模な補強工事は、塔の安定性を飛躍的に向上させました。北側の地盤を掘り、鉛の重りを設置するなど、様々な工法が用いられ、傾きの進行を食い止めました。
The Leaning Tower of Pisa, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located in the famous Piazza del Duomo (which has been registered as a World Heritage site since 1987) and is the bell tower of the Cathedral of Santa Maria Assunta. The tower houses seven bells.
So, why is the Leaning Tower of Pisa tilted? The answer lies in the problems with the foundation of the land where it was built.
Construction began in 1173, but long before that, the area was a marshland close to the sea, making the ground very soft. The foundation of the tower was only about 3 meters deep. This depth was insufficient to support the weight of the tower, as it was difficult to dig deeper foundations with the technology available at the time. The builders noticed the tilt early on and temporarily halted the construction. However, about 100 years later, work resumed. To counter the tilt that had started during construction, the upper part of the tower was slightly curved in the opposite direction of the lean. This adjustment improved the tower’s balance and stability. Over the years, the tilt caused the ground beneath the tower to compress, increasing its strength. Additionally, large-scale reinforcement works carried out from the late 20th century into the early 21st century dramatically improved the stability of the tower. Various methods were used, including digging the ground on the north side and installing lead weights to halt the progress of the tilt.
Thank you for reading.
新潟エリアM.L